CBD & WHY IT’S THE NEW DAILY VITAMIN
WHEN PURCHASING THC AND/OR CBD PRODUCTS, YOU MAY SEE THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN TWO TERMS: BROAD SPECTRUM & FULL SPECTRUM…BUT WHAT DOES THAT MEAN AND WHY ARE THEY DIFFERENT? KEEP READING TO FIND WHICH IS THE BEST SOLUTION FOR YOU!
Is CBD legal? Federally, hemp-derived CBD products containing less than 0.3% THC are legal, but they may still be prohibited under certain state laws. Conversely, marijuana-derived CBD products are illegal at the federal level but allowed in some states. It is important to check local legislation, particularly while traveling. Within the realm of cannabidiol (CBD) extract, there are three primary types, namely full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate. The key distinctions lie in the presence of other naturally occurring plant compounds within the extract.
COMPARISON BETWEEN FULL-SPECTRUM AND BROAD-SPECTRUM CBD:
CBD, one of the primary compounds found in the cannabis plant, is abundant alongside THC.The key distinction between full-spectrum and broad-spectrum CBD lies in their composition of compounds.Full-spectrum CBD CAN contains multiple naturally occurring extracts from the cannabis plant, including terpenes and other cannabinoids, with THC levels up to 0.3%.Broad-spectrum CBD also includes various cannabis plant compounds but typically lacks THC entirely. CBD ISOLATE:
CBD isolate is the third prevalent form of CBD, consisting solely of pure CBD without any other compounds from the cannabis plant.It's important to note that while these terms carry significance, the regulation surrounding CBD and related terminology is limited, leading to potential misuse or interchangeability by certain manufacturers.EXTRACTION:
CBD extraction from the cannabis plant primarily employs three methods:1. Carbon dioxide (CO2) extraction: This method separates CBD oil from the plant using CO2. It is popular for CBD products and enables the production of high-concentration CBD.2. Steam distillation: Manufacturers utilize steam to extract oil from the plant material. While commonly employed for extracting essential plant oils, it is not as efficient as the CO2 method.3. Solvent extraction: This method can effectively extract CBD but may leave behind solvent residue, posing potential health risks. It can also impact the extract's flavor.An emerging technique called lipid extraction is gaining traction as some companies aim to avoid CO2 and solvents.Following extraction, the resulting CBD oil is referred to as full-spectrum. CBD sourced from hemp will have THC concentrations of 0.3% or less.To obtain CBD isolate, the extract undergoes a cooling and purification process. Further processing yields a crystalline isolate known as CBD crystals.
PROS AND CONS OF FULL-SPECTRUM CBD:
PROS:
1. Wide Range of Cannabinoid Compounds: Full-spectrum CBD contains various cannabinoid compounds from the cannabis plant, potentially enhancing its therapeutic effects.2. Entourage Effect: The presence of multiple compounds, including terpenes, may contribute to an entourage effect, where the combined effects of cannabinoids and terpenes work synergistically, potentially improving the overall effectiveness of CBD.3. Potential Health Benefits: Full-spectrum CBD has been associated with various potential health benefits, including anti-seizure properties, antioxidant effects, anxiety relief, pain reduction, anti-inflammatory effects, and relief from muscle spasms.4. Dental Health Benefits: Some research suggests that the flavonoids and terpenes in CBD could have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, or antimicrobial properties, potentially benefiting dental health conditions like toothaches, gingivitis, or dental caries.CONS:
1. THC Content: Full-spectrum CBD products contain low levels of THC, typically below 0.3% as required by federal law. While this amount is unlikely to cause intoxication, concentrated products or higher doses may lead to a mild euphoric effect.2. Risk of Positive Drug Test: Full-spectrum CBD products containing THC may pose a risk of triggering a positive result on a drug test, as THC is one of the substances screened for in such tests.It's important to note that the pros and cons listed above are general considerations, and individual experiences and reactions to full-spectrum CBD may vary.
PROS AND CONS OF BROAD-SPECTRUM CBD:
PROS:
1. Additional Compounds: Broad-spectrum CBD products contain various additional compounds from the cannabis plant, including cannabinol (CBN), cannabichromene, and terpenes, which may contribute to potential health benefits.2. Potential Health Effects of CBN: CBN, found in broad-spectrum CBD, is associated with potential antibiotic, anti-seizure, and anti-inflammatory properties.3. Entourage Effect: Similar to full-spectrum CBD, broad-spectrum CBD products can potentially benefit from the entourage effect, where the combination of cannabinoids and terpenes may enhance overall effectiveness.CONS:
1. Lack of THC: Broad-spectrum CBD does not contain THC, which means it may not provide the same benefits as full-spectrum CBD. THC is known to have its own potential therapeutic effects.2. Risk of Positive Drug Test: While most broad-spectrum CBD products do not contain THC, some may still have trace amounts. This may pose a risk of triggering a positive result on a drug test that screens for THC.It's important to consider that individual experiences and reactions to broad-spectrum CBD may vary, and the pros and cons mentioned above are general considerations.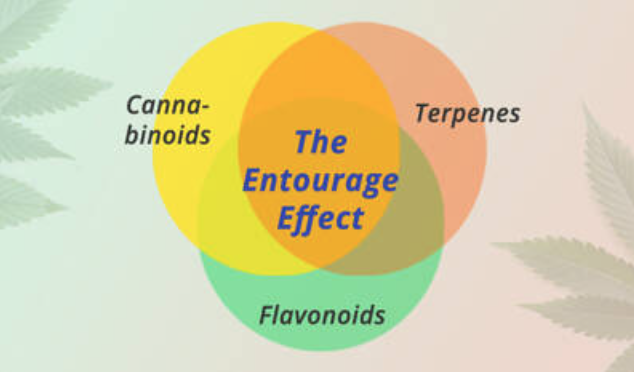
THE “ENTOURAGE EFFECT”: TERPENES COUPLED WITH CANNABINOIDS FOR THE TREATMENT OF MOOD DISORDERS AND ANXIETY DISORDERS
Major depressive and anxiety disorders are commonly encountered in psychiatric practice and affect a significant number of individuals worldwide. Depression, in particular, affects hundreds of millions of people, with approximately 20% of the population experiencing it during their lifetime. The condition manifests through a wide range of symptoms and can have a profound impact on society due to the distress and disruption it causes. If left untreated, depression can even pose life-threatening risks. Anxiety disorders often coexist with depressive states and frequently occur alongside other mental and physical conditions.
Bipolar disorder (BD) is characterized by alternating between depressive and manic mood states, with a diagnosis of Bipolar 1 possible even after one episode of mania. It is relatively common, affecting around 1% of the general population, and is considered a chronic condition that may require lifelong treatment. Like anxiety and depressive disorders, the underlying pathophysiology of BD remains unknown. Many patients with these disorders show resistance to treatment and exhibit high levels of comorbidity with other psychiatric conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder. The resistance to treatment, coupled with an inability to work and frequent hospitalizations, leads to significant costs for healthcare and national economic systems.
First-line medications for mood disorders primarily target the monoaminergic system, involving noradrenergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmitters. This system plays a crucial role in emotional and behavioral symptoms, including mood, vigilance, motivation, fatigue, and psychomotor agitation or retardation. However, the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, and emerging research suggests multiple neurochemical targets beyond the monoaminergic system. Despite current treatments providing relief to about 60-70% of cases, a substantial number of patients do not find relief, and the rate of remission is disappointingly low. Furthermore, many individuals who respond to treatment experience negative side effects, such as dry mouth, abdominal pain, sexual dysfunction, increased anxiety, violent tendencies, and even suicidal thoughts. Unfortunately, there is no universally effective treatment or cure for these disorders. Therefore, there is a need for new pharmacological approaches that can alleviate adverse effects and effectively treat non-responsive patients.
Recent studies, including randomized controlled trials, have indicated that certain phytocannabinoids found in specific Cannabis sativa varieties have the potential to alleviate anxiety and other mental disorders. This review focuses on the effects of cannabinoids and explores the possibility of enhancing their activity on psychiatric symptoms through the addition of terpenes and terpenoids. The method involved searching Pubmed and Google Scholar for relevant literature from the past 25 years, encompassing cannabinoids, terpenes, and their association with anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorders, including studies with contradictory results.
The "entourage effect" refers to the suggested positive synergy achieved by combining terpenes with cannabinoids, resulting in a greater overall effect than the sum of their individual contributions. In other words, the combined effect is more significant than what each component would achieve alone. The concept of the entourage effect in Cannabis was first introduced by Mechoulam and Ben-Shabat, who hypothesized that other inactive biological compounds present alongside primary endogenous cannabinoids enhance their activity. Russo expanded on this idea, describing botanical synergy, wherein a dominant molecule, such as cannabinoids, is complemented by other plant derivatives, including terpenes, flavonoids, and other inactive substances, to achieve a maximal pharmacological effect. Russo's review of several studies demonstrated that whole plant extracts had a superior effect compared to purified cannabinoids.
To the best of our knowledge, the innovative combinations of terpenes and cannabinoids have not been explored in previous scientific research. Incorporating different cannabis-derived compounds provides an opportunity to potentially mitigate the adverse effects associated with existing antidepressants and mood stabilizers when addressing mood disorders. This approach holds significant promise, especially for patients who do not respond well to or are unable to adhere to conventional treatments. By exploring these novel combinations, there is a potential to revolutionize the treatment landscape for mood disorders and offer alternative options for those in need.
SOURCES:
HTTPS://WWW.MEDICALNEWSTODAY.COM/ARTICLES/FULL-SPECTRUM-CBD-VS-BROAD-SPECTRUM-CBD#DIFFERENCES
HTTPS://WWW.NCBI.NLM.NIH.GOV/PMC/ARTICLES/PMC7324885/


